Registry Credentials
In the Admin Dashboard, you can set up private registry credentials for your Okteto instance. These credentials are automatically used by Okteto for various developer operations like building and deploying, so developers don't need direct credential access. Once set, all developers can access the registries through Okteto without additional steps. Additionally, you have the option to manage these credentials via Kubernetes CRDs provided by Okteto.
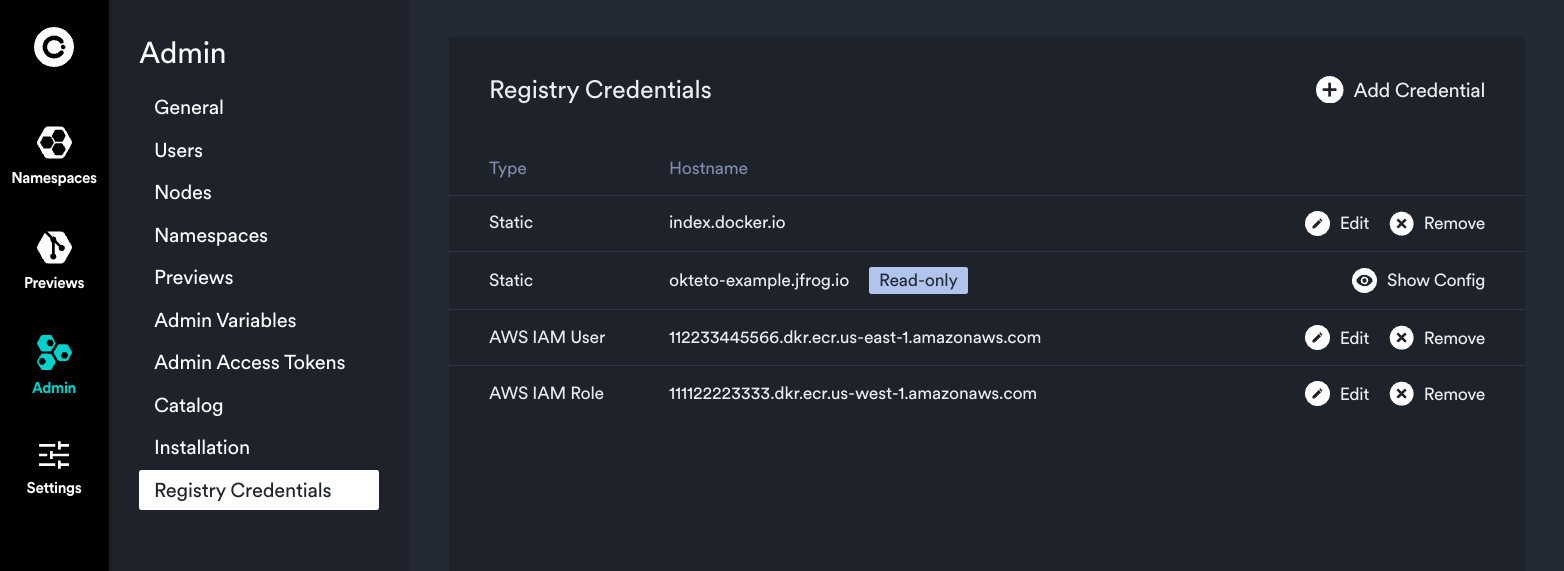
Registry credentials are applied to the Okteto Build service to allow private base image in your Dockerfiles.
Add Registry Credentials
Click in the Add Credential button on the top right corner of the Registry Credentials view. A dialog will let you choose the type of credentials, your registry hostname, and your username and password:
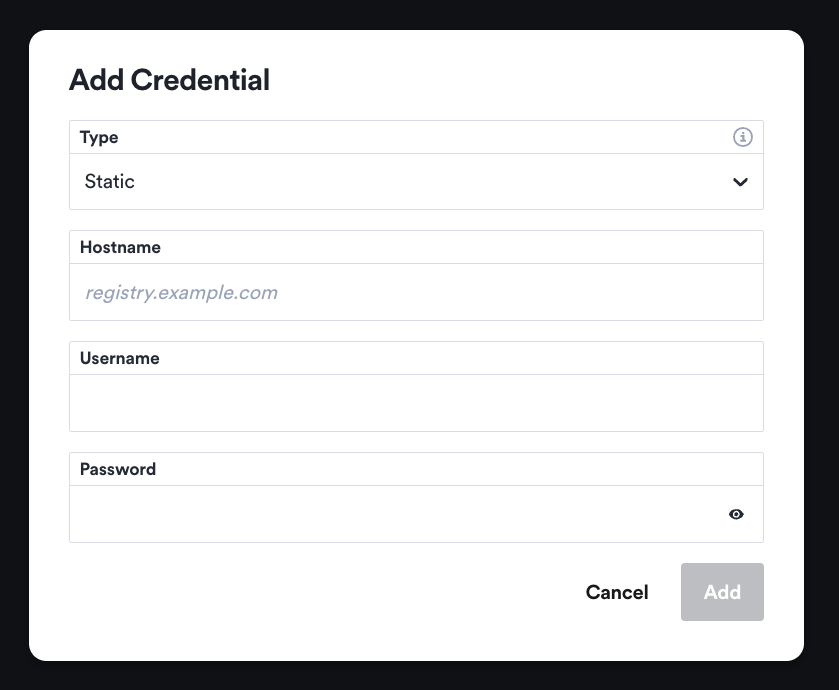
There are three types of registries that can be configured in Okteto:
- Static - credentials use a username and password, ideal for platforms like DockerHub.
- AWS IAM User - Provides credentials for Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) using an Access Key and a Secret Key. Okteto will exchange an ECR temporary token with AWS using these credentials.
- AWS IAM Role - Provides credentials for Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) using a predefined AWS IAM Role. Okteto will exchange an ECR temporary token with AWS using OIDC federation
Follow our guides below to learn how to retrieve your registry credentials:
For other registries, if the registry is exposed in a port other than the default http(s) 80/443, the port must be included in the Hostname, eg: my-registry.com:5000.
Finally, click the Add button of the dialog. Your registry credentials might take a few minutes to propagate to all of the components in the cluster.
Edit Registry Credentials
The Registry Credentials view enables you to rotate your registry credentials. Click on the Edit button on the right of every registry credential. For sensitive data you will only see the last few characters as a hint to verify the value:
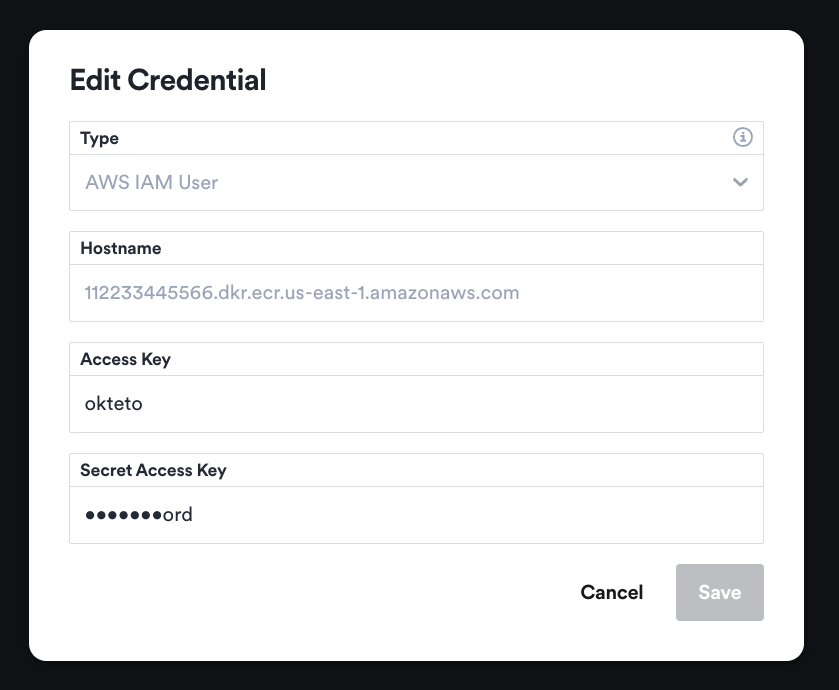
Click the Save button in the dialog. Your registry credentials might take a few seconds to propagate to all of the components in the cluster.
Remove Registry Credentials
The Registry Credentials view enables you to remove registry credentials if you don't need them anymore. Click on the Remove button on the right of every registry credential. A confirmation dialog will be shown:
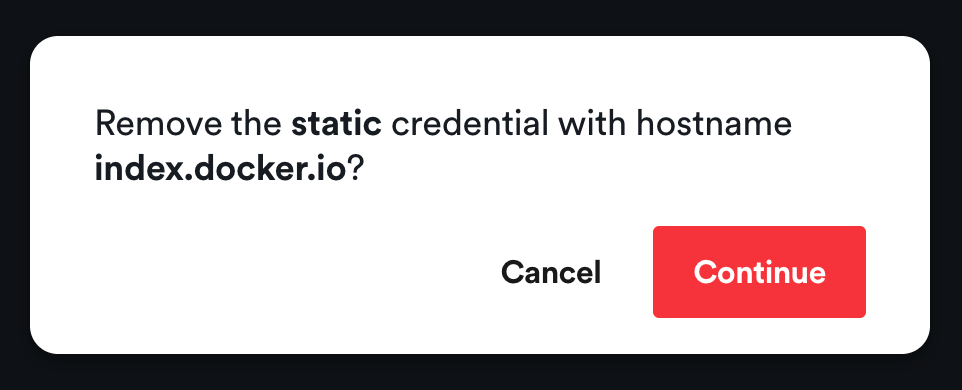
Click Continue in the confirmation dialog and your registry credentials will be removed from the cluster.
Manage Registry Credentials using CRDs
You can also manage your Registry Credentials using CRDs. This is useful, for example, if you have your own mechanism to provision credentials/secrets in your cluster.
To make sure Okteto is able to access your private registries, you can check if they are available from the Admin dashboard. If you add credentials using CRDs they will be displayed in the UI, but they can't be modified from the UI. If you want to manage them from the UI, they must be created from there.
How it works
Okteto runs a dedicated Kubernetes Controller to manage Registy Credentials. As part of this process, the Controller creates and manages a Docker Config JSON secret in the Okteto namespace.
This secret is called okteto-dockerconfig-static and is always up to date with your Registy Credentials, either through the UI or using CRDs.
This docker config secret is used as a pull secret in installer jobs, in case your installer job image is private.
The docker config secret is added in all namespaces and preview environments created by Okteto, with the name okteto-regcred.
okteto-regcred is injected as a pull secret to all pods by the Okteto Webhook to allow the deployment of private images.
By default, the okteto-regcred only contains credentials for the Okteto Registry
To disable this behavior set the following configuration in your helm values:
regcredsManager:
pullSecrets:
enabled: false
If this behavior is disabled, Okteto can write this secret on every node which allows Kubelet to pull private images at deployment time. To enable this behavior set the following configuration in your helm values:
daemonset:
configurePrivateRegistriesInNodes:
enabled: true
daemonset.configurePrivateRegistriesInNodes.enabled is deprecated and it will be removed in Chart 1.23